What Is an ETF in Crypto?

Content
The cryptocurrency market is becoming increasingly attractive to institutional and retail investors. One key innovation has been ETFs, which allow you to invest in cryptocurrencies without having to purchase them outright. This article will explain what bitcoin ETF is and how ETFs impact the financial world.
What is an ETF in simple words?
An ETF is an Exchange-Traded Fund that allows investors to purchase shares in a fund that tracks the value of certain assets such as stocks, bonds or cryptocurrencies. In the case of cryptocurrencies, an ETF provides access to digital assets without requiring you to purchase them directly.
So, an ETF is, in simple terms, a way to invest in cryptocurrencies through a fund that tracks their value without buying and holding the digital assets personally.
What Are Cryptocurrency ETF For?
Many large investors need help to purchase digital assets directly due to the lack of legal regulation and the complexities involved in storing them safely. In this context, ETFs offer them a more familiar and convenient way to enter the cryptocurrency market.
How Does It Work?
Cryptocurrency ETFs allow investors to participate in the market for digital assets without directly owning them. The fund goes through several steps to take this. Let’s examine each of them.
Launch
The first step is for the issuing company to apply with the SEC (U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission) to launch the ETF bitcoin. In preparation for the launch of a new product, the issuing company offers shares of a future ETF to a primary investor, providing seed capital for the fund. This capital is used to purchase the assets that will form the basis of the ETF, be it stocks, bonds or cryptocurrencies. Once the fund is formed, the ETF shares become available for trading on the open market, allowing investors to purchase them on the exchange like regular stocks by participating in changes in the value of the underlying assets on which the fund is based.
ETF Сollateralization
Once the primary investor provides capital, the issuing company uses those funds to purchase the assets that make up the fund’s underlying. In the case of cryptocurrency ETFs, such as the Spot Bitcoin ETF, the collateralization is that the fund owns a certain amount of bitcoins, which is reflected in its shares. Each ETF asset issued represents a share in those bitcoins or other underlying assets.
Asset Storage
One key difference between spot Bitcoin ETFs and traditional funds is the choice of custodian or platform that stores the real BTC used to back the fund. Some ETFs rely on exchanges for storage, while others prefer to use their digital asset divisions to secure the fund’s cryptocurrency.
Some experts believe concentrating so much Bitcoin on one platform carries significant risks. For example, while the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission has already approved these ETF funds, it is simultaneously pursuing litigation with Coinbase, accusing the company of illegally trading tokens that the regulator classifies as securities. Some ETFs are expected to diversify their asset custody platforms in the future.
ETF Pricing
The pricing of spot ETF BTC is based on the management of Bitcoin reserves and the issuance of shares whose value is directly tied to the price of BTC. These funds operate through the interaction of two key groups of participants— market makers and authorized participants.
The role of market makers is to accurately track the ETF’s share price relative to the market value of Bitcoin. They continually buy and sell shares of the fund, capitalizing on small discrepancies between the current market price of the shares and their fair value based on the bitcoin price. This process helps adjust the price of the ETF, bringing it closer to the value of the underlying asset.
There are also authorized participants—companies like Jane Street Capital, Virtu Financial, and JPMorgan Chase—that control the amount of shares the fund issues and redeems. They respond to changes in investor demand: If demand for ETF shares increases, they contribute to the fund, for which they receive new baskets of shares. This leads to an increase in the supply of shares on the market, and new bitcoins are added to the fund’s reserves.
When investors start selling shares en masse, authorized participants return them to the fund and receive money. This reduces the supply of shares on the market and lowers the fund’s bitcoin reserves.
What Types of Crypto ETFs Are There?
There are several types of cryptocurrency ETFs: Cryptocurrency futures ETFs, which invest in cryptocurrency futures contracts (ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF); spot crypto ETFs (iShares Bitcoin Trust), which directly hold cryptocurrency (e.g., Purpose Bitcoin ETF); multi-cryptocurrency ETFs that track multiple cryptocurrencies simultaneously (e.g., Bitwise 10 Crypto Index Fund); and blockchain ETFs that invest in stocks of companies related to blockchain technology (Amplify Transformational Data Sharing ETF).
Bitcoin ETFs
The road to Bitcoin (BTC) ETF approval in the U.S. has been long and fraught with many regulatory hurdles. The first application for a spot bitcoin ETF was filed in 2013 by brothers Cameron and Tyler Winklevoss, known for their cryptocurrency projects. Dozens of BTC ETF applications have been rejected over the years. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), responsible for approving the spot ETF, has been cautious, citing risks related to market volatility, liquidity, and the potential for manipulation.
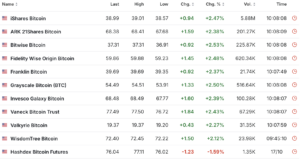
The SEC officially approved the first Bitcoin spot ETF in January 2024. After more than a decade of waiting and numerous rejections, this was a milestone for the cryptocurrency industry. The approval paved the way for 11 spot bitcoin ETFs, including funds from major players like BlackRock, ARK, Fidelity, and Grayscale.
List of all cryptocurrency ETF funds. Source: https://investing.com/discover/bitcoin-etfs
Ethereum ETF
The SEC approved the first Ethereum spot ETF (ETH ETF) to begin trading on July 23, 2024. Nine funds, including Grayscale, BlackRock, and Fidelity, received approval. Ether, the second-largest cryptocurrency after Bitcoin, rose 1% after trading began. ETF Ethereum are strengthening cryptocurrencies’ position in traditional finance, but the same hype as with bitcoin ETFs is not expected, as ether is more difficult for investors to understand.
Solana ETF
Currently, the Solana ETF has yet to be approved by the SEC. VanEck and 21Shares have filed applications for a spot Solana ETF, which would allow investors to directly buy shares that reflect the value of SOL in 2024. However, the approval process faces several challenges, including the need for a futures market for Solana and the possible recognition of the SOL token as a security, which complicates regulation. A decision on these applications will likely be made in 2025, depending on changes in the regulatory environment
How to Buy ETF and Invest?
To invest in crypto ETF, you must first open a brokerage account on any platform that supports exchange-traded fund trading. Afterward, fund your account and select the right ETF depending on your goals—equity, bond, or cryptocurrency-related funds. Enter the ETF ticker symbol and specify the number of shares to buy. Once the cryptocurrency ETF transaction is finalized, it will appear in your ETF investment portfolio and you can track its performance to make further decisions.
Conclusion
The development of cryptocurrency ETFs holds promise for the large-scale adoption of digital assets in investors’ portfolios. ETF crypto adoption, regulation, and simplified access make cryptocurrencies a more reliable tool for investment diversification, allowing the use of proven stock trading mechanisms.
FAQ
A spot ETF is an exchange-traded fund that directly tracks the price of an underlying asset, such as a cryptocurrency, without using futures or derivatives.
A bitcoin ETF is an exchange-traded fund that allows investors to indirectly own it through traditional stock exchanges without directly buying the cryptocurrency.