What Is A Private Key In Crypto And How Does It Work?

Content
Blockchain is a bottomless ocean of information, where each address has a public and private key. Blockchain security is based on cryptographic algorithms, where the private key opens a virtual vault and provides access to digital assets. In this article, we will explain how do crypto private keys work, delve into creating a private key, and discover how a simple combination of letters and numbers can guarantee the security of users’ assets.
What Is a Cryptocurrency Private Key?
A private key is a set of randomly generated characters that gives you access to assets on the blockchain and is used for signing transactions. Someone who knows your private key can access all your crypto assets and sign transactions (perform any action on the blockchain).
How the Private Key Is Used in Crypto?
The private key is used to sign transactions and interact with blockchain assets (i.e., log into the wallet). Suppose you lost the device on which your cryptocurrency wallet was installed. This does not mean that all your funds are also irretrievably lost. You can regain access to the wallet using a private key. Consider importing a wallet using MetaMask as an example.
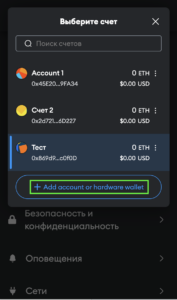
Follow the instructions:
- Click on the account selection box and the “Add account or hardware wallet” button.

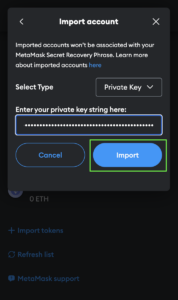
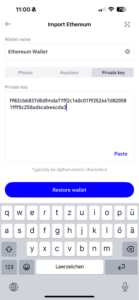
- Select “Import account,” insert your private key, and click “Import”.
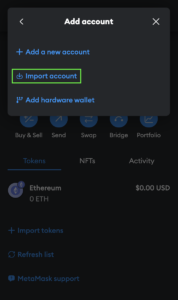
- Congratulations. All you need to do is add the tokens you had in your wallet. To do this, click “Import tokens.”
Methods of Storing Private Keys
The ways you can store your private keys are limited only by your imagination. The main thing is that this place should be reliable and accessible only to you. For example, it can be a cell in a bank vault, a home safe, digital media, or a cloud for private key storage. Some people even use stenography in digital images. For example, you have a favorite photo where you can encrypt a private key using various utilities and decode it if necessary. Some programs allow you to hide data inside audio files.
Depending on your needs and level of security, there are several basic ways and where to store private keys:
Custodial is a type of wallet in which a third party, such as an exchange, manages your private key. In such wallets, the user does not have control over their private keys; they remain on the side of the wallet or exchange. With the help of such wallets, you can conveniently and quickly convert crypto.
Non-custodial is a type of cryptocurrency wallet that does not store users’ keys. Using such wallets, you can manage your private keys personally. Although users of such wallets have complete control over their assets, they are also responsible for the safety of their private keys and, accordingly, funds.
Cold refers to a method of storing offline private keys. This includes hardware wallets. They not only generate the private key, seed phrase, and PIN code for the device but also isolate the key from internet connections and malicious software.
Hot involves crypto key storage online. This can include web wallets, exchange wallets, or software wallets for computers and mobile devices. Hot wallets are more vulnerable to online threats and are recommended for storing small amounts.
It is also worth mentioning brain wallets and paper wallets, which are the most secure and, at the same time, unreliable ways to store private keys. Brain wallets involve memorizing private keys or seed phrases, while paper wallets hold them on paper. In the first case, a person may forget their key. In the latter case, the sheet with the private key can be lost, damaged, or compromised by a photo.
How Do Crypto Private Keys Work?
It all starts with the generation of a private key. This key is a random sequence of letters and numbers unique for each address. With the help of cryptographic functions, the corresponding public key is calculated from the private key. Computing the private key from the public key is impossible, although it is generated based on the private key.
Let’s look at the mechanics of how a private key works on the example of a single transaction in a blockchain. Suppose George wants to send one Bitcoin or USDT to Emma.
- George needs Emma’s public key (sending address) to send a transaction. In addition, he needs to specify the right amount of cryptocurrency (one Bitcoin) and initiate the transaction.
- Hashing of the data takes place. This transaction contains various information, including the sender’s address (George), the recipient’s (Emma), and the transfer amount. A unique string (hash) is created to secure the transaction data.
- George’s private key receives the baton. It creates a digital signature of the transaction.
- Now that the transaction is signed, it is sent to the blockchain network. Validators authenticate the transaction using George’s public key and the digital signature. The transaction is considered valid if the signature is correct and matches the transaction data.
- Once the transaction is validated and signed, it is included in a new block on the blockchain, which is then added to the overall blockchain.
- The transaction has been successfully added to the blockchain, and George and Emma’s balances are updated. George loses one Bitcoin, and Emma receives this amount at her address (with fees deducted).
Public Key vs Private Key
A private key and a public key are two halves of a whole. Without them, you wouldn’t be able to send and receive transactions. The private key is confidential. It is used to decrypt data and sign transactions, confirms ownership of funds on the blockchain, and allows you to manage the funds on the cryptocurrency address. You cannot recover the private crypto key once you lose it (only with a recovery phrase). Therefore, it cannot be shown or shared with third parties.
On the contrary, the public key can be seen by everyone — it is a user identifier in the network and is also used to encrypt transaction data and verify signatures. Knowing only the public key can not give access to the wallet; you can safely share it to get cryptocurrency to your address.
Even though the public key can always be generated from the private key, it has no reverse effect. Simply put, knowing the private key based on the public key is impossible.
Crypto Private Key Examples
The private key to the wallet is almost impossible to find — all thanks to sophisticated encryption algorithms. In short, before creating a cryptographic key, an algorithm generates a random set of digits (called entropy). The algorithms then encrypt the entropy, and a mnemonic phrase is created. A seed — a modified version of the mnemonic phrase is created from it. Based on the seed, private key encryption is generated.
The scheme of private key generation looks like this:
Entropy → mnemonic phrase → seed → crypto keys
For example, an Ethereum private key looks like this:
f982cbb837d0dfdda77ff2c160c01f9252667d820581ff95c250ad6cabe4cda3
Cryptography is also used to create a public key based on a private key.
For example, Ethereum’s public key always starts with “0x,” and it looks like this:
0x0083301AcD7dfF66715c432B91553C2F45A08CcC
What Are the Benefits of Private Key?
The main advantage of a private key is that, if properly stored, it is virtually impossible to compromise it. In addition, the private key allows you to confirm the author of the transaction, as it acts as a signature.
It is essential to mention the possibility of importing the key into other wallets. The wallet itself is not bound to your private key; it is just an interface to interact with. This is what importing the same private key into MetaMask and Trust Wallet looks like:
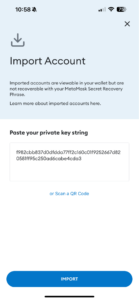
Source: MetaMask Wallet Source: Trust Wallet
You can also make the import with Seed-phrase — 12-24 English words from a unique dictionary. It is used to back up the key.
Risks and Challenges Associated with Private Keys
Unrecoverability. It is impossible to recover a private key from a public key. People use a variety of ways to find or remember where the private key lies. Some look for their devices through trash cans, while others try to recreate their copy using artificial intelligence. We recommend storing your private keys securely to avoid doing either of them.
Attackers often use social engineering to trick people into revealing their private keys. For example, they may write to you under the guise of wallet technical support and ask you to send your private key. The legends can be different, but the goal is the same — to lure out the private key and take possession of the funds.
Malware and attacks. Network traffic interception attacks (Man-in-the-Middle), malicious browser extensions, online address generators, phishing, fraudulent sites — a short list of ways to steal your private key. There have been cases where people were given hardware wallets with third-party software. When the person enters their private key, it automatically becomes available to the attacker.
How can you minimize the risks?
- Don’t buy wallets from dubious stores at an undervalued price. It’s much safer to order directly from the manufacturers’ official stores;
- Regularly and timely update the software on all your devices and wallets;
- Don’t keep private cryptocurrency keys on your computer;
- Do key rotation from time to time and move your assets from one address to another;
- Don’t use online address generators. Do it only through your wallet interface.
- Never share your private key with anyone.
What Is the Best Way to Store Private Keys?
Custodial storage. A simple and convenient method, as a third-party service provider, such as an exchange, manages private keys for the user. This option suits beginners because it does not require experience or high responsibility. There is no risk of losing keys — if you forget your password to the exchange or wallet, you can quickly recover it with the help of support. In addition, exchanges usually have a wide cryptocurrency list.
Non-custodial storage. It is Suitable for those who want to manage their keys independently and have full access to their assets. As a rule, these are already experienced users who know about the disadvantages of custodial storage. In this case, there are no third parties — only the user controls his keys and assets.
Hotstorage is suitable when you use funds frequently. You should not store many assets on hot wallets, as they are vulnerable to Internet threats. Hot wallets are used on decentralized exchanges, smart contracts, and blockchain applications.
Coldstorage is perfect for buying crypto and keeping it for a few years. This method is usually used to store large amounts of cryptocurrencies. Yes, cold hardware wallets are not as fast and convenient as hot wallets, but they will provide maximum protection for your assets.
The Bottom Line
The private key works in tandem with the public key. The encrypted private key is coded through several methods, including symmetric, asymmetric, and hashing. The private cryptocurrency key is used to decrypt the information. With the help of a digital signature, the sender can be easily confirmed. You can access your assets with a private key from any wallet, which should be stored securely.
FAQ
It is a set of letters and numbers generated randomly. A private key is important because it gives users access to assets and is used to decrypt data and create digital signatures.
In the case of custodial storage (exchanges, platforms), private keys are stored by third parties. Non-custodial storage means self private key management with full access to the assets. Keys can be stored in offline and online environments.
You can recover it with a seed phrase, but access to the funds will be lost forever if it is also lost. If someone gets your secret key, they can dispose of your assets.
- What is Crypto Technical Analysis? How to Analyze Price Movements in the Cryptocurrency Market?
- Faucet Crypto: What Is It, and How Does It Work?
- What Does Burning Crypto Mean?
- A Beginner’s Guide to Day Trading Crypto
- What Is Crypto Volatility?
- How to Get a Crypto License in 2024
- What is the Wyckoff Method and How to Apply It in Crypto Trading?